Today, India stands at a critical juncture. The country aims to accelerate its growth across the spectrum. In such a scenario, effective land governance is an essential aspect that can usher in more equitable development, optimised urban planning, and efficient revenue generation. So, what must India leverage to achieve these? Cadastral mapping, which is a geospatial tool rapidly gaining prominence among state governments, municipal bodies, and private enterprises alike.
Over the years, Mapex, has established itself as a leader in geospatial intelligence, and has been instrumental in enabling this transformation across India. Through this article, we explore how cadastral mapping helps improved land governance and leads to a more transparent and efficient property taxation process.
What is Cadastral Mapping?
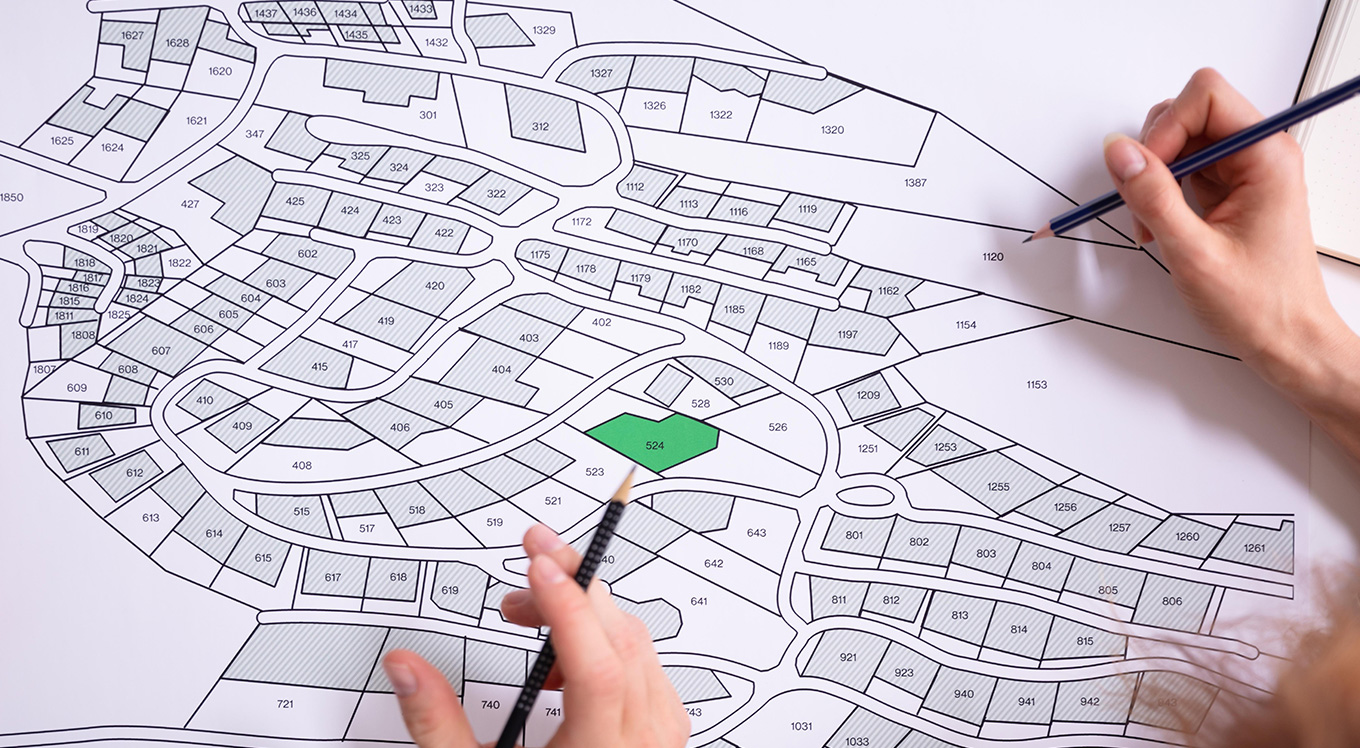
Before we move forward, first, let us break down what cadastral mapping is. The process is the creation of detailed, large-scale maps that comprehensively outline land parcels, ownership, boundaries, tenure, and land use. Unlike topographical or general GIS maps, cadastral maps are legally authoritative and are crucial in setting the foundation of transparent land records. As a part of this process, each land parcel is uniquely identified and linked to ownership, taxation, and legal rights.
At its core, a cadastre brings together maps and location data with details like who owns the land, how it’s used, and what legal rights exist. This creates a clear, standardised, and digital record of land.
Why Cadastral Mapping Matters in India
In this section, we take a look at some of the key impact areas of cadastral mapping, especially in the Indian context:
1. Fragmented and Outdated Land Records
A critical area slowing down India’s progress is the country’s land administration system, which is still rooted in legacy systems, paper-based records, and a lack of clarity when it comes to managing the records across government departments. To exemplify this by data, a 2021 NITI Aayog report suggests that over 66% of civil cases in Indian courts are related to land. A combination of errors in record-keeping overlapping claims, and inaccurate boundaries contribute to this crisis.
With cadastral mapping, we will be able to deploy a digital, tamper-proof system for maintaining and updating land records. Combining this initiative with the Digital India Land Records Modernisation Programme (DILRMP) will help governments and citizens to access real-time, accurate data, which will result in less confusion, litigation, and administrative delays.
2. Boosting Urban and Rural Property Tax Collection
An important contributor to any growing economy is the taxation associated with Urban Local Bodies (ULBs). However, in India, there is a massive challenge in property tax collection. India’s property tax-to-GDP ratio stands at a mere 0.16%. This number is much lower than the OECD average of 2.2%. Such low numbers are not a reflection of a casual approach towards taxation but rather because of inefficient valuation methods, outdated property databases, and weak enforcement.
With Cadastral mapping, ULBs can access:
- Accurate property listings
- Realistic valuation based on location, usage, and size
- Identification of unauthorised or unregistered properties
- Transparent tax slabs based on real spatial data
3. Accelerating Infrastructure Development and Urban Planning
One of India’s key priorities currently is urbanisation, primarily due to the fact that the country’s urban population is expected to cross 600 million by 2036. Such a jump in the population will create a lot of pressure on urban authorities to plan for growth and sustainability. Cadastral data can help across projects of different scales, whether it is allocating land for metro corridors or planning greenfield townships.
Using cadastral layers with demographic and utility datasets, planning bodies can:
- Predict future infrastructure scenarios
- Conduct precise impact assessments
- Design data-driven rehabilitation plans
- Ensure infrastructure development adheres to ownership rights
Over the years, Mapex has built a powerful GIS system that makes it easy to combine different data layers accurately, helping governments plan ahead instead of reacting later. Such advanced planning will certainly improve our governance methodologies.
4. Faster Legal Resolution of Land Disputes
India’s courts are overloaded with land-related cases, many of which drag on for years due to unclear boundaries, missing documents, or overlapping claims.
Cadastral mapping helps speed up these legal processes by providing:
- Clear and reliable proof of land ownership and boundaries
- Protection against fake or duplicate land titles
- A solid base for fair arbitration and mediation
- Faster decisions in land acquisition and compensation cases
The Role of Mapex in Cadastral Transformation

At Mapex, we aspire to leverage our extensive experience in end-to-end geospatial solutions, including high-resolution satellite imagery, drone-based surveying, GIS analytics, and custom cadastral platforms for improved Indian governance. Our strengths include”
- Accurate Surveying: Our drone-based aerial surveys offer up to 5 cm accuracy, leading to reduced boundary errors.
- Smart Integration: Our systems are capable of integrating with government systems such as BhuNaksha, e-GRAMSwaraj, and property tax platforms for easy data transfer.
- Conflict Resolution: Our mapping system helps resolve disputes by visualising overlaps in ownership and rights with historic claims.
- Ai-Powered Analytics: We leverage AI and machine learning models to detect unauthorised constructions and changes in land use.
The Broader Economic Impact
1. Easier Access to Credit
Banks and NBFCs need verified land records to give out home and farm loans. With clear ownership details from cadastral data, landowners can get loans more easily. This reduces dependence on informal moneylenders and boosts local economies.
2. Encouraging Private Investment
Businesses in sectors like manufacturing, real estate, and logistics often face delays because of unclear land records. Cadastral mapping removes confusion, lowers risk, and speeds up land acquisition. In fact, India ranked 154th in the World Bank’s 2019 'Registering Property' index. While reforms have started, modern cadastral systems are key to improving this further.
3. Better Legal and Environmental Oversight
Cadastral maps help enforce zoning rules, detect encroachments, and monitor environmental changes. For example, when combined with forest data, they help forest departments track illegal deforestation with accurate, location-based proof.
The Way Forward: From Static Records to Dynamic Governance
The next step isn’t just digitising maps but making cadastral systems dynamic. This includes real-time updates for:
- Property mutations (sales, inheritance, gifting)
- Construction or demolition changes
- Land use shifts (e.g., agricultural to residential)
- Legal encumbrances and liens
By aligning cadastral mapping with India’s broader digital governance ecosystem, linking with Aadhaar, property tax IDs, and land registration, authorities can create a “single source of truth” for land. This not only reduces fraud but builds trust among citizens and investors.
Conclusion
Cadastral mapping is not just a technical solution. It is a governance necessity for an India that aspires to accelerate its development. For a country where land continues to be both an economic asset and a socio-political point of conflict at times, investing in cadastral modernisation will unleash a different era of transparency, efficiency, and inclusivity at scale.
At Mapex, we stand at the crossroads of geospatial technology and policy transformation. Through data-driven cadastral solutions, we aim to support India’s journey towards stronger land governance and sustainable growth.



Share this Article :
Published at: 20-08-2025